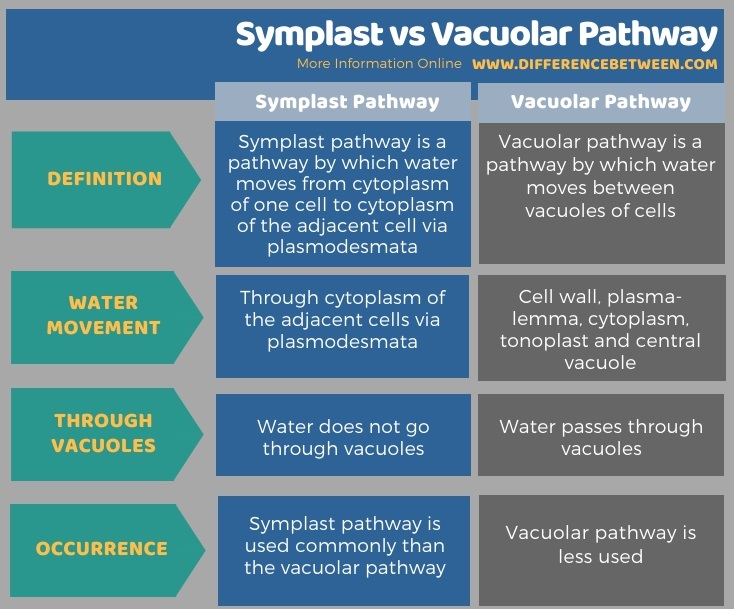
The most important difference between the symplast pathway and the vacuolar pathway is that the symplast pathway doesn’t allow any water to enter the vacuoles, but the vacuolar pathway does allow water to enter the vacuoles.
What is Symplast Pathway?
The symplast pathway is the pathway through which water and solutes move through the cytoplasm and cell-to-cell connections of plants. It is important for the distribution of water and nutrients throughout the plant and the movement of signaling molecules and hormones.

The symplast pathway involves the movement of substances through plasmodesmata, which are small channels that connect the cytoplasm of plant cells to each other. Plasmodesmata allow for the movement of substances between cells without crossing the cell membrane and can be selectively permeable, meaning that they can allow certain substances to pass through while preventing others from passing through.
The symplast pathway is active, meaning that it requires energy to move substances through it. It is also selective, meaning that only certain substances can pass through the cytoplasm and cell-to-cell connections. This allows the plant to control which substances are transported and where they are transported to.

The symplast pathway is important in the transport of substances in the phloem, which is the tissue responsible for the transport of sugars and other substances from the leaves to the rest of the plant. It is also important in the distribution of water and nutrients throughout the plant, as substances can move through the symplast pathway from cell to cell and reach different parts of the plant without having to move through the apoplast pathway.
Overall, the symplast pathway plays an important role in the distribution and transport of substances in plants and is essential for the proper functioning and growth of the plant.
What is Vacuolar Pathway?
The vacuolar pathway is a route of substance transport within a plant that involves the movement of substances into and out of the plant cell vacuole. The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled organelle found within plant cells that serves several important functions, including the storage of excess nutrients and waste products, the maintenance of cell shape and turgor pressure, and the regulation of the plant’s pH.
The vacuolar pathway begins when substances enter the cell through the plasma membrane and are transported into the vacuole through a process known as endocytosis. This process involves the formation of vesicles, which are small, membrane-bound structures that enclose the substance being transported. The vesicles then fuse with the vacuolar membrane (tonoplast), releasing their contents into the vacuole.
Substances can also be transported out of the vacuole through a process known as exocytosis, which involves the reverse of endocytosis. In exocytosis, vesicles formed within the vacuole fuse with the tonoplast and release their contents into the cytoplasm of the cell.
The vacuolar pathway is important for the storage of excess nutrients and waste products, as well as for the maintenance of cell shape and turgor pressure. It is also involved in the transport of larger molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids, and is less selective than the symplast pathway, allowing a wider range of substances to pass through the tonoplast.
What are the Similarities Between Symplast and Vacuolar Pathway?
- Symplast and vacuolar pathways are two of the three main types of water movement pathways through plant cells.
- In both pathways, water passes through the cytoplasm of the cell.
- Water moves by osmosis in both pathways.
Symplast VS Vacuolar Pathway
The symplast pathway and the vacuolar pathway are two different routes that substances can take as they are transported within a plant. Here are the top ten differences between the two pathways:
- Location: The symplast pathway involves the movement of substances through the cytoplasm and plasmodesmata of plant cells, while the vacuolar pathway involves the movement of substances into and out of the plant cell vacuole.
- Substance movement: The symplast pathway allows for the movement of substances within a single cell or between cells, while the vacuolar pathway allows for the movement of substances within a single cell or between cell vacuoles.
- Type of substances: The symplast pathway is mainly used for the transport of small molecules, such as sugars and amino acids, while the vacuolar pathway is mainly used for the transport of larger molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids.
- Membrane transport: The symplast pathway involves the transport of substances across the plasma membrane, while the vacuolar pathway involves the transport of substances across the tonoplast (vacuolar membrane).
- Selectivity: The symplast pathway is selective, meaning that it only allows certain substances to pass through the plasma membrane, while the vacuolar pathway is less selective, allowing a wider range of substances to pass through the tonoplast.
- Regulation: The symplast pathway is regulated by specific transport proteins, while the vacuolar pathway is regulated by vesicle fusion and fission.
- Energy expenditure: The symplast pathway requires the expenditure of energy, while the vacuolar pathway does not.
- Function: The symplast pathway is mainly involved in the transport of nutrients and signaling molecules, while the vacuolar pathway is mainly involved in the storage of excess nutrients and waste products.
- Plant development: Both the symplast and vacuolar pathways play important roles in plant development, but they do so in different ways. The symplast pathway is important for cell-to-cell communication and the distribution of nutrients, while the vacuolar pathway is important for the storage of excess nutrients and waste products.
- Examples: Some examples of substances that are transported through the symplast pathway include sugars, amino acids, and signaling molecules, while some examples of substances that are transported through the vacuolar pathway include proteins, nucleic acids, and pigments.
KEY-POINTS
- The symplast pathway involves the movement of substances through plasmodesmata, which are small channels connecting the cytoplasm of plant cells to each other.
- The symplast pathway is important for the transport of substances in plants and helps the substances reach different parts of the plant without having to move through the apoplast pathway.
- The vacuolar pathway is a route of substance transport within a plant that involves the movement of substances into and out of the plant cell vacuole.
- The vacuolar pathway begins with the formation of vesicles, which are small, membrane-bound structures that enclose substances being transported. These vesicles fuse with the vacuolar membrane, releasing their contents into the vacuole.
- The symplast pathway and the vacuolar pathway are used for the transport of substances within and between plant cells, as well as between cell vacuoles. The symplast pathway involves the transport of substances across the plasma membrane, while the vacuolar pathway involves the transport of substances across the tonoplast. Both pathways play an important role in plant development but in different ways. The symplast pathway and the vacuolar pathway transport substances between cells.
Summary
Two of the three water transport pathways in plant cells are the symplast and vacuolar pathways. Water moves along the symplast pathway from the cytoplasm of one cell to the cytoplasm of the next cell via plasmodesmata.
In the vacuolar pathway, water travels through the cytoplasm of cells as it passes between their vacuoles. Plant cells use the symplast pathway more frequently than the vacuolar pathway because it has lesser resistance. Thus, the difference between the vacuolar pathway and the symplast pathway is summarised.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by the apoplast pathway?
Through the apoplast pathway, water moves along the adjacent wall of the epidermis and the cortex, but it does not enter the cytoplasm.
What is an apoplast?
The system of adjoining cell walls that continuous is known as the apoplast. It is a reference to the area outside of the plasma membrane where molecules are able to freely diffuse inside that space.
What is the importance of the Casparian strip?
The Casparian strip is a band of water-resistant tissue that can be found on the side walls of the root endodermis. The strip blocks the path of water that would otherwise reach the pericycle, which is critical for the process of inducing root pressure.
Reference:
- “Movement Of Water In Roots: 3 Pathways (With Diagram)”. Biology Discussion, 2020, Available here.
- 2. “Symplast Pathway”. Embibe.Com, 2020, Available here.
- Apoplast pathway. Available Here
- https://socratic.org/questions/what-are-some-substances-that-are-transported-through-the-cell-membrane-by-simpl
- https://mcqtimes.com/which-form-of-transport-through-the-plasma-membrane-requires-the-expenditure-of-energy-by-the-cell/
Image Courtesy:
1. “Apoplast and symplast pathways” By Jackacon, vectorised by Smartse – Apoplast and symplast pathways.gif, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
