The iodine test is used to differentiate polysaccharides from monosaccharides and disaccharides.
The Iodine Test is a simple yet effective chemical method used to detect the presence of starch and other substances. It relies on the reaction between iodine and specific compounds, producing a distinct color change.
What is Iodine?
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol “I” and atomic number 53. It is a dark purple solid and is part of the halogen group. Apart from its applications in the laboratory, iodine plays a crucial role in human health, particularly in the functioning of the thyroid gland.

Principle
Different carbohydrates, for example, starch, form colored adsorption complexes with iodine due to the adsorption of iodine on the polysaccharide chains.
The intensity of the color is dependent on the length of the unbranched or linear chain accessible for the complex formation. Iodine forms a complex with starch to give deep blue-black color.
Glycogen (highly branched polysaccharide) gives a red color with iodine.
Reagents Required for Iodine Test
- Iodine solution: Dissolve Iodine (1.0 g) and potassium iodide (2.0 g) in 300 ml of distilled water.
- Starch solution (1%)
Preparation of the Test Solution
First, prepare the iodine test solution by dissolving iodine crystals in water or an aqueous potassium iodide solution.
This step ensures the formation of triiodide ions, which enhance the reaction with starch and other target compounds.
Procedure
- Add 2 ml of the sample to a test tube.
- Add 1-2 drops of iodine solution.
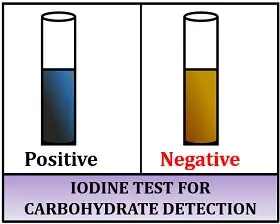
- The formation of a blue-black color indicates the presence of starch.
Result:
The formation of a blue-black color indicates the presence of starch.
Applications of the Iodine Test
The iodine test finds numerous applications in various fields, primarily due to its ability to detect starch. Let’s explore some common uses of this test.
Detecting the Presence of Starch
The iodine test helps determine whether a food item contains starch in cooking and food processing. This information is valuable for dietary considerations, quality control, and optimizing production processes.
By applying the iodine test, one can quickly identify starch-rich ingredients or monitor the conversion of starch during cooking or baking.
Testing for the Presence of Iodine in Solutions
Apart from detecting starch, the iodine test is also employed to identify the presence of iodine in solutions.
This application is handy in analytical chemistry and forensic science, where iodine may serve as a reactant or a trace element indicative of specific processes or reactions.
Identifying the Presence of Glycogen
Glycogen, a polysaccharide similar to starch, is animals’ primary energy storage molecule. The iodine test can also detect glycogen’s presence, allowing researchers to study energy metabolism and storage in various biological systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Iodine Test
Like any analytical technique, the iodine test possesses its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore these:
Advantages
- Simplicity: The iodine test is simple, requiring minimal equipment and expertise.
- Speed: Results can be obtained within minutes, making it time-efficient.
- Cost-effective: The materials required for the iodine test are readily available and affordable.
Disadvantages
- Limitations: The iodine test may have limitations in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and interference from other compounds.
- Subjectivity: Interpreting color changes in the iodine test can be subjective, requiring careful observation and comparison to known standards.
- Potential hazards: Iodine can be toxic and should be handled with care. Appropriate safety precautions should be followed when working with iodine and its solutions.
Safety Precautions and Handling
When working with iodine and its solutions, it is essential to prioritize safety. Here are some general safety precautions:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves and safety goggles.
- Handle iodine and its solutions in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood.
- Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes. In case of accidental exposure, rinse thoroughly with water and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Dispose of iodine waste properly, following local regulations and guidelines.
FAQs about Iodine test
What are some typical applications of the iodine test?
The iodine test finds applications in food science, quality control, forensic analysis, and biological research, primarily for detecting the presence of starch and iodine.
Can the iodine test be used to detect the presence of sugars?
The iodine test is specific to starch and may not reliably detect the presence of sugars. Alternative tests such as Benedict’s or Fehling’s test are commonly used for sugar detection.
Are there any alternatives to the iodine test for detecting starch?
There are alternative methods for detecting starch, including enzymatic assays and spectroscopic techniques. These methods offer increased sensitivity and specificity in starch analysis.
Can the iodine test be performed on solid samples?
Yes, the iodine test can be performed on solid samples by extracting starch from the sample using appropriate solvents before applying the test.

Thank you for any other great article. The place else may just anybody get that kind of info in such an ideal means of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I’m at the look for such information.
It’s really a nice and helpful piece of info. I’m satisfied that you simply shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.