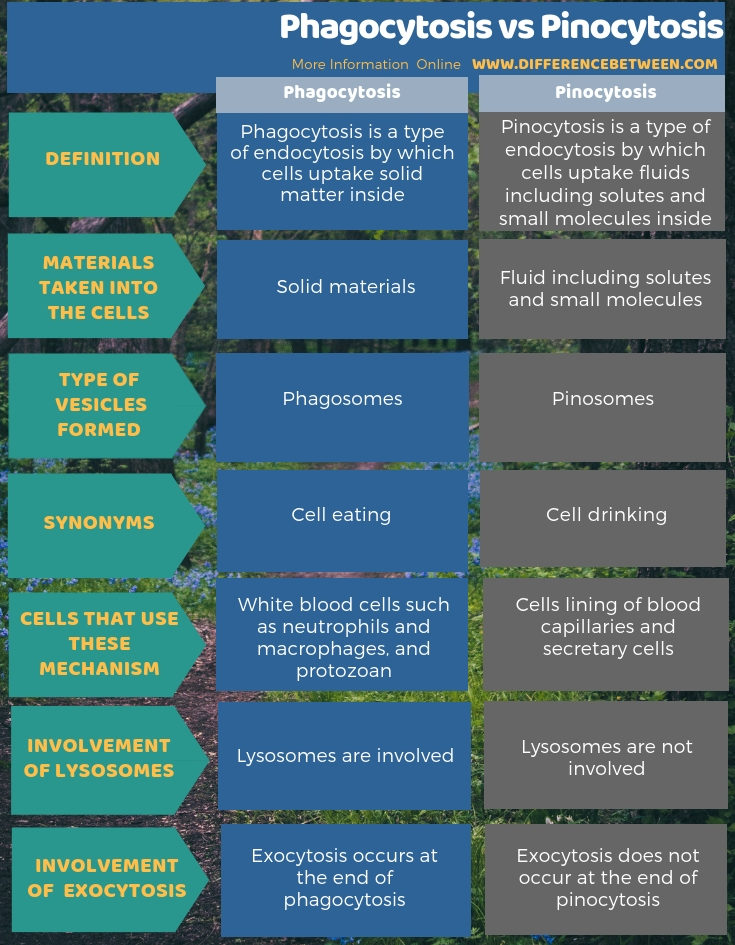
Phagocytosis and pinocytosis are two types of endocytosis, which is the process by which cells take in materials from their surroundings.
Endocytosis is a process that allows cells to take in macromolecules and other suspended particles, such as cell components, macromolecular aggregates, and foreign particles. Specifically, this process is responsible for bringing these substances into the cell. The process through which cells export material outside of the cell is known as exocytosis. This process is the complement to endocytosis.
There are two types of endocytosis based on the nature of the particles that are taken into living cells. They are phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
Phagocytosis involves the internalization of solid particles, such as bacteria or debris, by specialized cells called phagocytes. Pinocytosis involves the internalization of small droplets of extracellular fluid and its dissolved substances.
Main Differences – Phagocytosis vs Pinocytosis
- Phagocytosis is carried out by phagocytes, while pinocytosis can occur in many types of cells.
- Phagocytosis involves the formation of a phagosome, while pinocytosis involves the formation of a pinosome.
- Phagocytosis requires the participation of enzymes called hydrolytic enzymes, while pinocytosis does not.
- Phagocytosis is a rapid process that occurs in response to specific stimuli, while pinocytosis is a continuous process.
- Phagocytosis is more efficient at internalizing larger particles, while pinocytosis is more efficient at internalizing smaller molecules.
What is Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a process by which a cell engulfs and destroys foreign materials, such as bacteria and other pathogens, or worn-out cell parts. It is an important part of the body’s immune system, helping to protect the body from infection and disease. The cell responsible for phagocytosis is known as a phagocyte. Phagocytes are found throughout the body and can be either fixed or mobile.
The process begins when a phagocyte recognizes and binds to a target molecule on the surface of the foreign material. The phagocyte then forms a pouch around the material, known as a phagosome, and draws it into the cell. The phagosome then fuses with a lysosome, a membrane-enclosed organelle that contains digestive enzymes.
The enzymes break down the foreign material, releasing nutrients and other molecules that can be used by the cell. The remaining material is then expelled from the cell in the form of waste.
Phagocytosis is also known as cell eating in single-celled organisms. Most protists like amoeba also uptake nutrients by phagocytosis. Essential nutrients can be taken into the cell by phagocytosis. The uptaking of nutrients often does not produce waste material. Amoeba phagocytosis is shown in the figure.

What is Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis is a type of endocytosis, a process by which cells take in substances from their environment by enclosing them in small vesicles or pockets within the cell membrane. Pinocytosis specifically refers to the uptake of small particles and molecules that are suspended in the extracellular fluid, such as ions, nutrients, and signaling molecules.
Pinocytosis occurs through the formation of small, dynamic invaginations or indentations in the cell membrane, which is called pinocytic vesicles. These vesicles form around the particles or molecules that the cell wants to take up, and then pinch off from the membrane to form a separate compartment inside the cell.
The vesicles containing the particles or molecules are then transported to endosomes, which are organelles within the cell that is specialized for sorting and processing the substances that have been taken up.
Pinocytosis plays an important role in the physiological processes of many types of cells, including cells in the immune system, blood vessels, and the gastrointestinal tract. It allows cells to take up and utilize small molecules that are necessary for their function, and also allows them to respond to signaling molecules and other stimuli from their environment. Pinocytosis is shown in figure 2.

What are the Similarities Between Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis?
- Phagocytosis and pinocytosis are two types of endocytosis.
- Both methods take in materials through the plasma membrane by forming vesicles
Difference Between Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis
Nature of the particles or molecules being taken up:
- Phagocytosis involves the uptake of large particles or organisms, such as bacteria, fungi, or cells that have died or been damaged. These particles are often too large to be taken up by pinocytosis.
- Pinocytosis involves the uptake of small particles and molecules that are suspended in the extracellular fluid, such as ions, nutrients, and signaling molecules. These particles are often too small to be taken up by phagocytosis.
Mechanism of uptake:
- Phagocytosis occurs through the formation of a phagosome, which is a large, cup-shaped invagination in the cell membrane. The phagosome engulfs the particle or organism and then fuses with lysosomes, which are organelles within the cell that contain enzymes that can digest the particle or organism.
- Pinocytosis occurs through the formation of small, dynamic invaginations or indentations in the cell membrane, which is called pinocytic vesicles. These vesicles form around the particles or molecules that the cell wants to take up, and then pinch off from the membrane to form a separate compartment inside the cell.
Role in physiological processes:
- Phagocytosis plays a critical role in the immune system, as it allows immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages to engulf and destroy foreign invaders and cells that have become damaged or diseased.
- Pinocytosis plays an important role in the physiological processes of many types of cells, including cells in the immune system, blood vessels, and the gastrointestinal tract. It allows cells to take up and utilize small molecules that are necessary for their function, and also allows them to respond to signaling molecules and other stimuli from their environment.
Conclusion – Phagocytosis vs Pinocytosis
Phagocytosis and pinocytosis are two types of the endocytosis process, in which the cell absorbs substances from the extracellular fluid. During phagocytosis, big solid particles are ingested, which are then broken down by lysosomal enzymes.
Dead cells and bacterial-like pathogens can be eaten by phagocytosis, and the waste products can be eliminated via exocytosis. Consequently, phagocytosis contributes to the cell’s defense. Extracellular fluids are ingested during pinocytosis, resulting in the formation of tiny vesicles.
With the aid of enzymes contained in lysosomes, phagocytosis is engaged in the digestion of the ingested material. In pinocytosis, however, there is no digestion, but ingested substances are easily absorbed. Consequently, the primary distinction between phagocytosis and pinocytosis is the quality of the material ingested by each phase.
Reference:
- Lennartz, Michelle R. “Phospholipases, and Phagocytosis.” Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 31 Mar. 2017.Cooper, Geoffrey
- M. “Lysosomes.” The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 31 Mar. 2017.
- Alberts, Bruce. “Transport into the Cell from the Plasma Membrane: Endocytosis.” Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 31 Mar. 2017.
- Cooper, Geoffrey M. “Endocytosis.” The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 31 Mar. 2017.
- “Pinocytosis.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 20 Nov. 2014, Available here.
- “Phagocytosis.” Khan Academy, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
- “Amoeba phagocytosis” By Miklos – Wikimedia commons (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
- “Pinocytosis” By Jacek FH – modified Image: Endocytosis types.SVG, author Mariana Ruiz Villarreal LadyofHats, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia

I discovered your weblog site on google and examine a number of of your early posts. Continue to maintain up the excellent operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading extra from you in a while!?