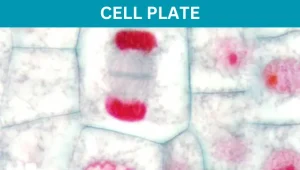
Cell Plate – Structure, Formation and Function
As land plants undergo cell division, a Cell Plate structure is formed within their cells. Land plant cells are unique because they have a cell wall made of rigid sugars surrounding their cell membranes, unlike animal cells. Besides protecting the … Read more