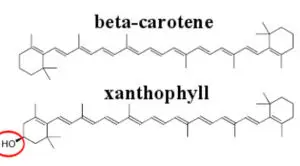
Carotenoids structure function and biosynthesis
Carotenoid Carotenoid is any of a large class of over 600 organic pigments, including the carotenes and xanthophylls, that are terpenoids. Carotenoids are lipid compounds that are universally present in nearly all higher plants, fungi, and bacteria. They are usually red, orange, yellow or brown … Read more