What are the Similarities Between Plasma and Serum?
- Both plasma and serum are present in the blood.
- They are vital components of the blood.
- Both contain metabolites, electrolytes, proteins, and antibodies.
- The process of centrifugation can isolate both of these from the blood.
- Both are fluids.
- They have more than 90% of water.
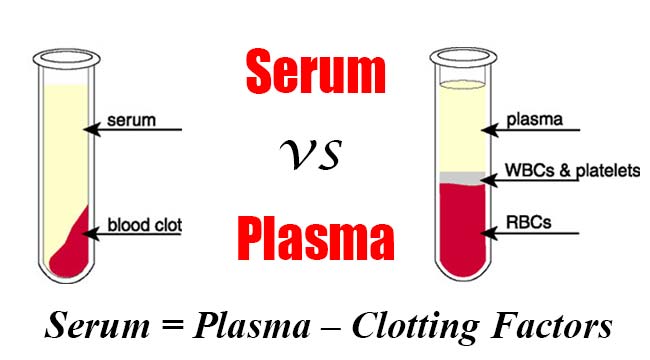
What are the Differences Between Plasma and Serum?
- Composition: Plasma is the liquid portion of the blood that contains proteins such as albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. The serum is the liquid portion of the blood that is left after the blood has clotted and the clot has been removed. It does not contain fibrinogen or other clotting factors.
- Formation: Plasma is formed when blood is collected in tubes that contain an anticoagulant, such as heparin or EDTA. The serum is formed when blood is collected in tubes that do not contain an anticoagulant and is allowed to clot, after which the clot is removed to obtain the serum.
- Use in laboratory testing: Plasma and serum are both used in laboratory testing to measure the levels of various substances in the body, such as hormones, enzymes, and proteins. However, some tests require the use of plasma while others require the use of serum.
- Stability: Plasma is generally more stable than serum because it contains clotting factors that help to preserve the sample. Serum can be more prone to degradation due to the absence of clotting factors.
- Collection methods: Plasma is usually collected using a process called plasmapheresis, in which the blood is drawn from the body and separated into its different components using a machine. The serum is usually collected using a simple blood draw in which the blood is allowed to clot and the clot is removed.
- Use in transfusions: Plasma is often used in transfusions because it contains clotting factors and other proteins that can help to restore normal blood clotting in patients with bleeding disorders. The serum is not used in transfusions because it does not contain clotting factors.
- Volume: Plasma makes up about 55% of the volume of whole blood, while serum makes up about 40% of the volume of whole blood.
- Color: Plasma is typically yellow in color due to the presence of proteins such as albumin and globulins, while serum is typically straw-colored due to the absence of these proteins.
- Uses in medicine: Plasma is used in a variety of medical applications, such as plasma transfusions, the production of medications, and the treatment of bleeding disorders. Serum is also used in medical applications, such as the diagnosis of infectious diseases and the measurement of hormone levels.
- Storage: Plasma and serum can both be stored in a frozen state for long periods of time, but plasma must be frozen immediately after collection to prevent degradation. Serum can be stored at room temperature for a short period of time before it is frozen.
| Aspect | Serum | Plasma |
|---|---|---|
| Component | The serum is a component of blood and the circulatory system. | Plasma is a component of blood and the circulatory system . |
| Constituents | Serum contains metabolites, electrolytes, proteins and antibodies. | Plasma also contains metabolites, electrolytes, proteins and antibodies. |
| Isolation | The serum is isolated by the process of centrifugation. | Plasma is also isolated by the process of centrifugation . |
| Appearance | The serum is a fluid left after the coagulation process. | Plasma is also a fluid that can be extracted, |
Conclusion – Plasma vs Serum
We can say that blood is one of the most important parts of the body and helps in the transportation of nutrients, hormones, gases, vitamins, etc. and thus connecting each section. The blood contains three important components like-plasma, white blood, and red blood cells. We discuss the fundamental difference between plasma and serum and how can be they separated. We also consider their uses and importance.
Reference:
- ”Blood Serum.” Merriam-Webster. Merriam-Webster, n.d. Web. 27 May 2017. <https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/blood%20serum>.
- ”Medical Definition of Serum.” MedicineNet. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 May 2017. <http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=5470>.
- ”Plasma.” American Red Cross. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 May 2017. <http://www.redcrossblood.org/learn-about-blood/blood-components/plasma>.
- Hess, John R. “Conventional blood banking and blood component storage regulation: opportunities for improvement.” Blood Transfusion. Edizioni SIMTI — SIMTI Servizi Srl, June 2010. Web. 27 May 2017. <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2897192/>
Image Courtesy:
- “Blood-centrifugation-scheme” By KnuteKnudsen at English Wikipedia (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
