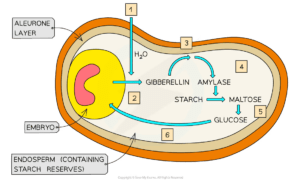
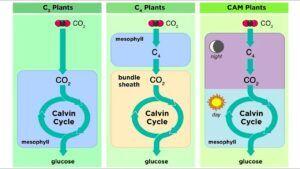
Cytokinins-Biosynthesis,Transport, Mechanism of action
Cytokinins Cytokinins are plant hormones that regulate various physiological processes in plants, including cell division, differentiation, and growth. They have a number of practical applications in agriculture, forestry, and horticulture. This group of hormones includes kinetin, benzyl amino purine, zeatin, … Read more