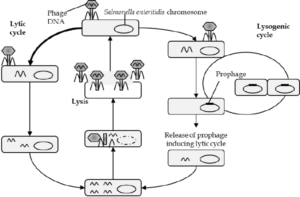
Bacteriophage Life Cycle
Bacteriophages (both singular and plural) are viruses that infect bacteria. They are diverse, both structurally and functionally, and are united solely by their occurrence in bacterial hosts. Many of these types of bacteriophage, called phage for short, are large and … Read more